Current issue
- Page Path
- HOME > Articles and Issues > Current issue
Original Papers
- Exploring Wild Bees Diversity in Seocheon Maeul-Soop: A Quantitative Study
- Sanghun Lee, Ohchang Kwon, Dong Su Yu, Jeong-Seop An, Na-Hyun Ahn
- GEO DATA. 2024;6(1):1-7. Published online March 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22761/GD.2024.0003

- 304 View
- 40 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Wild bees are important pollinators in the ecosystem, and it is important to monitor their abundance and diversity to characterize and conserve these pollinators. In this study, wild bees were collected from a Maeul-soop in Seocheon-gun, Chungcheongnam-do, Republic of Korea for 2 years from February 2019 to October 2020. From the survey, a total of 3,258 wild bees from 9 families and 57 species were collected over 2 years in the Maeul-soop. The most dominant species was the Andrena kaguya, followed by the Apis mellifera, the Eucera spurcatipes, the Seladonia aeraria, and the Lasioglossum sibiriacum. Monthly changes in the number of species and populations show that the number of species increased from February and peaked in August, and the population peaked in April and then decreased. In addition, in the list of wild bee species collected over the past 2 years, the Apidae was the largest with 16 species, followed by the Halictidae with 13 species and the Megachilidae with nine species. However, although there is only one species of Andrena kaguya in the Andrenidae, its population is 2,084, which is the largest among all wild bees investigated in this study. The results of this study will be useful in understanding the impact of pollinating insects due to climate change in the future.
- Vegetation Spatial Distribution on Taean Duung Wetland Protect Area
- Haeseon Shin, Sanghun Lee, Sangwook Han
- GEO DATA. 2024;6(1):8-13. Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22761/GD.2024.0004

- 206 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, we conduct for providing information on the status of vegetation space distribution in the Duung wetland protected area and to help manage the wetland protected area. To understand the spatial distribution of vegetation in Duung Wetland, used the results of surveys in 2019 and 2023. As a result of the study, the number of vegetation types increased by 4 from 20 to 24. Four communities were newly investigated, including the Utricularia tenuicaulis community, Pueraria montana var. lobata-Elymus tsukushiensis community, Spiraea prunifolia for. simpliciflora community, and Miscanthus sinensis var. purpurascens community. In accordance with the environment, the range of aquatic plant communities such as Trapa japonica community and Nymphaea tetragona var. angusta community increased, and the succession zone of cultivated land expanded dry grassland. The survey results can be used as basic data for systematic management of the Duung wetland protected area.
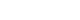
- The Cheonji Lake GeoAI Dataset based in Optical Satellite Imagery: Landsat-5/-7/-8 and Sentinel-2
- Eu-Ru Lee, Ha-Seong Lee, Sun-Cheon Park, Hyung-Sup Jung
- GEO DATA. 2024;6(1):14-23. Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22761/GD.2023.0055
- 210 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The variations in the water area and water level of Cheonji, the caldera lake of Baekdu Mountain, serve as reliable indicators of volcanic precursors. However, the geographical and spatial features of Baekdusan make it impossible to directly observe the water area and water level. Therefore, it is crucial to rely on remote sensing data for monitoring purposes. Optical satellite imagery employs different spectral bands to accurately delineate the boundaries between water bodies and non-water bodies. Conventional methods for classifying water bodies using optical satellite images are significantly influenced by the surrounding environment, including factors like terrain and shadows. As a result, these methods often misclassify the boundaries. To address these limitations, deep learning techniques have been employed in recent times. Hence, this study aimed to create an AI dataset using Landsat-5/-7/-8 and Sentinel-2 optical satellite images to accurately detect the water body area and water level of Cheonji lake. By utilizing deep learning methods on the dataset, it is reasonable to consistently observe the area and level of water in Cheonji lake. Furthermore, by integrating additional volcanic precursor monitoring factors, a more accurate volcano monitoring system can be established.
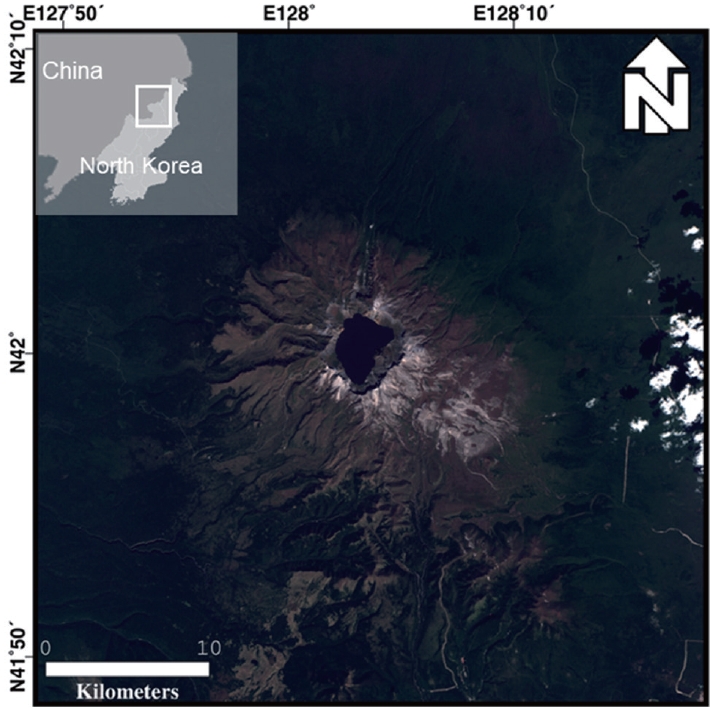
- Evaluation of Slope Stability on Dam Using Ground-based Interferometric Radar
- Seongcheon Park, Sanghoon Hong
- GEO DATA. 2024;6(1):24-31. Published online March 21, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22761/GD.2024.0001
- 407 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dams are man-made structures built to manage water resources efficiently and prepare for natural disasters such as droughts and floods. It requires careful and continuous inspection to prevent its failure. Research reported to assess dam stability using terrestrial surveys such as ground penetration radar, electrical resistivity tomography, and remote sensing methods such as space-borne synthetic aperture radar (SAR). Differential interferometric SAR (DInSAR) calculates the phase difference between two consecutive images acquired at separate times and has been widely utilized to detect surface displacement from volcanoes, earthquakes, and ground subsidence. However, space-borne InSAR applications have limitations in acquiring flexible data for specific dates or regions due to the revisit cycle of the orbital configuration and the fixed acquisition geometry. In this feasibility study, the slope stability of the dam was evaluated using the Gamma Portable Radar Interferometer-II (GPRI-II) which has the advantage of overcoming the limitation of satellite observations. The GPRI-II is a ground-based real aperture radar that operates in the Ku-band wavelength (~1.7 cm), providing convenient portability and installation for high spatial and temporal resolution. A total of 20 GPRI-II datasets were acquired for 22 minutes on June 7, 2023, at a dam in Jeollanam-do for the DInSAR application. The displacement calculation revealed an average displacement of approximately -0.36 mm at a randomly selected point, which is negligible. The average displacement of -0.17 mm was observed for the entire dam. Our results suggest that ground-based radar interferometry could assess the dam slope stability.
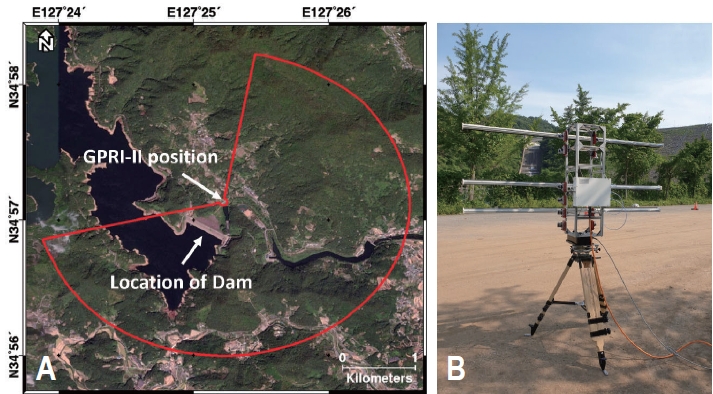
- Evaluation of Calibration Using Corner Reflector with Ground-Based Interferometric Radar
- Je-Yun Lee, Jeong-Heon Ju, Sang-Hoon Hong
- GEO DATA. 2024;6(1):32-42. Published online March 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22761/GD.2024.0002
- 276 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The accuracy of microwave remote sensing relies on the calibration of the radar measurement. It is important to estimate the radar cross-section (RCS) using a passive corner reflector (CR) or active transponder to evaluate the quality of imaging radar data. A strong and consistent RCS can be achieved by the acquisition of radar signals concentrated at specific angles during the CR calibration procedure. There are several types of CR depending on the shape and size such as triangular trihedrals, square trihedrals, dihedrals, spheres, or cylinders. In this study, we examine the RCSs using three types of CR with Ku-band ground-based real aperture radar equipment, the Gamma Portable Radar Interferometer-II. It can be easily deployed to acquire fully polarimetric radar observations. The initial experiment was conducted at Busan Sam-nak Auto Camping Site on November 1, 2023. The amplitude images show much higher backscattered radar signals at the CR location, whereas relatively lower power has been captured in the surrounding areas. The attenuation factors in the radar receivers could be useful to prevent saturation around the CR location at the line-of-sight direction. The experiment indicates that the different levels of the RCS measurements from three types of CRs could be utilized for calibration study with fully polarimetric radar observations.
Erratum
- Erratum to: Detailed Bathymetry and Seafloor Backscatter Image Dataset for Monitoring Ecosystem Environment: Southern Ulleungdo
- Soon Young Choi, Chang Hwan Kim, Won Hyuck Kim, Chan Hong Park
- GEO DATA. 2024;6(1):43-43. Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.22761/GD.2024.e001
- Corrects: GEO DATA 2023;5(4):364
- 671 View
- 12 Download

 GAIDAS
GAIDAS


 First
First Prev
Prev