Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > GEO DATA > Volume 5(1); 2023 > Article
-
Original Paper
원격 탐사 기반 일차생산 추정의 개선을 위한 남극 폴리냐 지역의 해색 위성 산출물 결측 복원 -
박진구1
 , 이성재2
, 이성재2 , 김정훈3
, 김정훈3 , 김현철4,*
, 김현철4,*
- Imputation of Ocean-color Product in Polynya Region of Antarctica for Primary Productivity Estimates
-
Jinku Park1
 , Sungjae Lee2
, Sungjae Lee2 , Jeong-Hoon Kim3
, Jeong-Hoon Kim3 , Hyun-Cheol Kim4,*
, Hyun-Cheol Kim4,*
-
GEO DATA 2023;5(1):8-14.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.22761/GD.2023.0002
Published online: March 28, 2023
1선임연구원, 극지연구소 원격탐사빙권정보센터, 인천광역시 연수구 송도미래로 26, 21990, 대한민국
2기술원, 극지연구소 원격탐사빙권정보센터, 인천광역시 연수구 송도미래로 26, 21990, 대한민국
3책임연구원, 극지연구소 생명과학연구본부, 인천광역시 연수구 송도미래로 26, 21990, 대한민국
4센터장, 극지연구소 원격탐사빙권정보센터, 인천광역시 연수구 송도미래로 26, 21990, 대한민국
1Senior Research Scientist, Center of Remote Sensing and GIS, Korea Polar Research Institute, 26 Songdomirae-ro, Yeonsu-gu, 21990 Incheon, South Korea
2Administrative Specialist, Center of Remote Sensing and GIS, Korea Polar Research Institute, 26 Songdomirae-ro, Yeonsu-gu, 21990 Incheon, South Korea
3Principal Research Scientist, Division of Life Sciences, Korea Polar Research Institute, 26 Songdomirae-ro, Yeonsu-gu, 21990 Incheon, South Korea
4Director, Center of Remote Sensing and GIS, Korea Polar Research Institute, 26 Songdomirae-ro, Yeonsu-gu, 21990 Incheon, South Korea
- Corresponding Author Hyun-Cheol Kim Tel: +82-32-760-5335 E-mail: kimhc@kopri.re.kr
Copyright © 2023 GeoAI Data Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 765 Views
- 38 Download
Abstract
- This study, focusing on the Antarctic polynyas, performed the imputation of chlorophyll-a concentration (Chl-a) dataset, which is one of the ocean color products mainly used for estimating primary productivity, using the Data Interpolating Empirical Orthogonal Function method and constructed accurate time-series data that excludes as much uncertainty as possible in long-term variability studies due to missing data. The polynya regions were classified into a total of 23 zones through quantitative criterions, and the statistical accuracy of imputation performance was 0.89 for R2 and 0.42, 0.24, and 0.15 for root mean square error, mean squared error, mean absolute error, respectively, on average, showing the ability to perform generally accurate reconstruction. Finally, the reconstructed Chl-a data showed a relatively stable fluctuation compared with standard satellite Chl-a data, and tended to be underestimated due to the expansion of the observable regions. We expect that securing these relatively stable and accurate estimates will be significantly different from the time-series data composed of standard Chl-a estimates, enabling more accurate variability and trend analysis.
- 남극에서 해빙, 고착빙, 해안선 등으로 둘러싸인 개방 수역인 폴리냐는 남극 대륙붕에 주로 나타나며 풍부한 영양염, 강한 성층, 계절적으로 개선된 빛 조건 등으로 인해 강한 식물플랑크톤 성장을 유발하고 이는 결국 폴리냐를 남극해에서 가장 생산성이 높은 지역으로 알려지게 하였다(Arrigo et al., 2015; Deppeler and Davidson, 2017; Gerringa et al, 2012). 더욱이 남극에서 일차생산을 담당하는 식물플랑크톤의 대사활동은 해당 지역뿐만 아니라 전 지구적인 생지화학적 순환 체계와 기후 변화에 영향을 미칠 수 있다. 이러한 중요성에도 불구하고 여전히 남극 폴리냐 시스템에서의 일차생산의 장기적인 변동성과 경향성에 대한 이해는 부족한 실정이다. 일차생산의 장기적인 변동성 및 경향을 이해하는 것은 결과적으로 남극 전체의 생물학적 요인으로 유발되는 환경 변화를 이해하기 위해서 중요하며, 나아가 전 지구적인 해양 시스템을 연구하는 데 필수적이다.
- 현재까지 현장 관측 및 모델링 실험을 통해서 많은 연구자들이 폴리냐 지역을 포함하는 남극 연안에서의 일차 생산의 미래 전망에 대한 다양한 증거를 제시한 바 있다(Gerringa et al., 2015; Kaufman et al., 2017; Leung et al., 2015; Rickard and Behrens, 2016). 그러나 이들 연구 대부분은 오직 모델에만 의존적으로 결과를 제시하거나 혹은 남극의 접근 제한성으로 인해 일부 국소한 지역 혹은 아주 짧은 기간 동안의 관측만으로 추정한 결과임으로 변동성 및 경향에 대해 제시된 결과의 신뢰성이 다소 부족하다.
- 위성 관측은 위에서 언급된 다른 방법보다도 상대적으로 광역적으로 높은 시공간 해상도를 지닌 자료를 생산하며, 특히 1997년부터 현재까지 지속적으로 운용되고 있는 해색 위성은 해양의 일차생산을 추정할 수 있게 하는 식물 플랑크톤 농도를 산출물로 제시하고 있다. 일부 연구는 이러한 해색 위성을 바탕으로 일차생산의 경향성 수행한 바 있다(Pinkerton et al., 2021; Smith and Comiso, 2008). 그러나 해색 위성의 가장 큰 제한점 중의 하나는 구름이나 안개의 존재에 따라 관측이 제한적이기 때문에 해색 위성 자료를 그대로 사용하는 것은 변동성 및 경향을 분석하는 데 상당한 불확실성을 안겨준다. 이를 극복하기 위한 방안으로 합성된 월간 자료를 사용하기도 하지만 소수의 일간 자료로 합성된 월간 자료의 신뢰성은 상당히 떨어진다. 일반적으로 해양의 일차생산력을 추정하는 방식은 해양 영역에서 일차생산성의 시공간적인 합으로써 표현하게 되므로 시간적인 해상도는 짧을수록 실제 추정치에 근접하게 되고 또한 일차생산이 발생하는 정확한 해양 공간 영역을 탐지해야만 높은 정확성을 가질 수 있다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 결측 추정을 위한 고차원적인 기법인 Data Interpolating Empirical Orthogonal Function (DINEOF)을 이용하여 남극 폴리냐 시스템에서의 식물플랑크톤 농도에 대한 결측 추정을 수행하고자 하였다.
1. 서론
- 2.1 조사지역
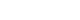
- 남극 폴리냐 시스템에서의 해색 산출물 결측 추정을 수행하기 위하여 폴리냐 지역에 대한 정의가 필요하였다. 폴리냐 탐지는 기본적으로 해빙 면적비(sea ice concentration) 자료를 바탕으로 수행되었으며, 해당 산출물은 일별 자료로 제공되며 25 km의 공간해상도를 지니고 있다. 본 연구에서 사용된 해빙 면적비는 Nimbus-7의 Scanning Multichannel Microwave Radiometer (SMMR)를 시작으로(1978-1987), Defense Meteorological Satellite Program을 Special Sensor Microwave/Imager (SSM/I; 1987-2007), Special Sensor Microwave Imager/Sounder (SSMIS; 2008-current)로 관측된 두 주파수(18, 36 GHz)의 밝기 온도를 이용하여 NASA Team 알고리듬으로 계산되었다. 해빙 면적비를 이용한 폴리냐를 선정하기 위해서 다음과 같은 기준들을 적용하였다(Table 1). 우선 남극 전 지역에 걸쳐 ice free days (IFD)를 계산하기 위하여 일간 해빙 면적비가 75% 미만으로 나타내는 지역을 탐지하고 모든 기간 6월부터 10월까지 누적된 일수를 계산한다(Li et al., 2016). 이러한 IFD가 20% 이상을 나타내는 지역을 선정하고, 폴리냐가 대부분 대륙붕 상에서 형성됨을 감안하여 수심이 2,000 m 이하인 지역 그리고 남위 65o 아래의 지역으로 정의하였다. 본 연구에서 수행한 복원 방식은 어느 정도의 유효한 픽셀이 확보되지 않으면 복원을 수행하는 데 제한이 따르므로 평균적인 자료 유효율(5.65%) 이상을 나타내는 지역을 선정하였다. 폴리냐는 매해 그 규모나 분포 특성이 어느 정도 가변적이므로 그러한 변화 특성을 감안할 수 있게 위에서 선정된 영역을 포함하도록 개략적인 영역을 선정하였다. 그 결과, 남극의 5개 섹터(로스해, 벨링스하우젠 및 아문젠해, 웨델해, 인도양, 서태평양)에서 총 23개의 폴리냐 영역이 설정되었다(Fig. 1). 정의된 폴리냐 지역 중 가장 넓은 지역은 polynya zone 02 (PZ02)로 로스해 폴리냐(Ross Sea Polynya)이다. 로스해 폴리냐는 남극 연안 폴리냐 중 가장 크고 오랜 기간 동안 지속되는 폴리냐로, 약 50,000-100,000 km2의 면적을 가지며, 로스 빙붕(Ross ice shelf)에서 불어나오는 강력한 활강 바람에 의해 형성된다. 또한 이 지역은 남빙양 전체 생산성의 약 28%의 높은 생산성을 나타내는 곳이다(Park et al., 2019).
- 2.2 해색 산출물: 엽록소 농도
- 본 연구에서 사용된 해색 산출물인 엽록소 농도는 유럽항공 우주국(European Space Agency)의 GlobColour project에서 생산된 다중 위성 합성 자료로서 약 4 km의 공간해상도를 지닌 일별 자료가 사용되었다. 다중 위성 합성은 SeaWIFS (Sea-Viewing Wide Field of View Sensor), MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer), MERIS (Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer), VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) 자료 등이 포함되어 있으며, Garver-Siegel-Maritorena 알고리듬을 통해서 합성되었다. 자료의 수집 기간은 SeaWIFS가 시작되는 1997년 8월부터 2021년 12월까지이며, 이들 자료 중 남극에서 식물플랑크톤이 번성하는 기간인 10월부터 3월까지의 자료만 사용되었다.
- 2.3 DINEOF
- DINEOF는 EOF를 기반으로 하는 결측 추정 방식으로 Beckers and Rixen (2003)에 의해 처음으로 제시되었다. 이후 해수면 온도, 염분, 엽록소 농도 등의 다양한 환경 변수에 대하여 다양한 지역에서 많은 연구자들에 의해 활용되어 왔다. 그러나 아직까지 북극을 제외한 남극지역에서의 활용 사례는 찾을 수 없으며, 이러한 낮은 활용성은 남반구 봄 및 여름철의 짧은 기간을 제외하고는 대부분 해빙, 구름, 낮은 태양 고도에 의해 대부분의 지역이 결측된다는 한계점으로 인한 것으로 사료된다. 따라서 계절 구분 없이 전체 자료에 대한 결측 추정은 상당한 제한이 따르므로 본 연구에서는 봄 및 여름철의 자료만으로 자료를 재구성하여 DINEOF를 수행하였다. DINEOF의 절차는 다음과 같이 간략하게 설명될 수 있다. 1) DINEOF 수행 이전에 입력 자료의 평균이 제거되고 누락된 값이 0으로 설정되며 독립적인 교차검증 자료 세트(각 폴리냐 지역별 전체 자료의 약 5%)가 식별되어 입력에서 제거된다. 2) EOF 모드는 특이값 분해(singular value decomposition) 기술을 사용하여 누락된 픽셀 값을 업데이트하며 교차검증을 위해 구분된 픽셀의 계산된 값과 실제 픽셀 값 사이의 정확도가 최적화될 때까지 반복적으로 분해를 수행하게 된다.
2. 본론
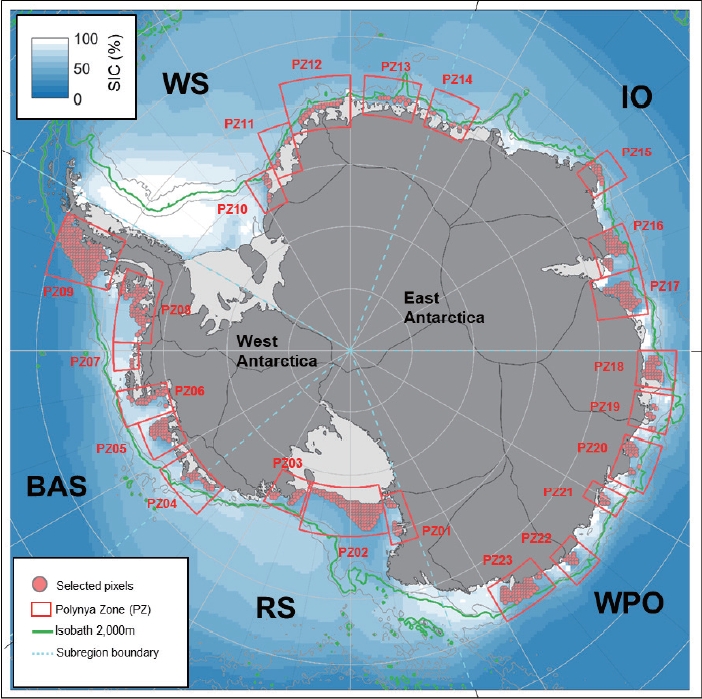
- 본 연구에서 구분된 23개의 폴리냐 지역에서의 결측 추정 결과에 대한 평가를 위해서 DINEOF에서 사용된 교차검증 자료 세트에 대한 통계적인 수치 평가를 Fig. 2에 제시하였다. 대부분의 지역에서 R2는 0.72-0.96의 범위를 보이며 평균 약 0.89로 높은 정확성을 보여주는 것으로 나타났다. Root mean square error, mean squared error, mean absolute error의 범위는 각각 0.06 (PZ15)-0.9 (PZ06), 0.00 (PZ15)-0.82 (PZ06), 0.02 (PZ15)-0.34 (PZ07과 PZ08)이며, 평균은 각각 0.42, 0.24, 0.15이다.
- Fig. 3은 남반구 봄 및 여름철 동안의 기존 위성 자료와 복원된 자료의 관측 유효 픽셀의 비율을 나타낸 것이다. 폴리냐 지역의 평균적인 유효 픽셀 비율은 2.7%이며, 복원된 자료의 평균 비율은 23.9%로 약 8.8배로 증가한 것을 확인하였다. 특히, PZ04에서 20.6배로 가장 높은 복원율을 보였으며, 인도양 섹터의 PZ17과 로스해 섹터의 PZ02에서 각각 5.3배, 5.8배로 상대적으로 낮은 복원율을 보였다.
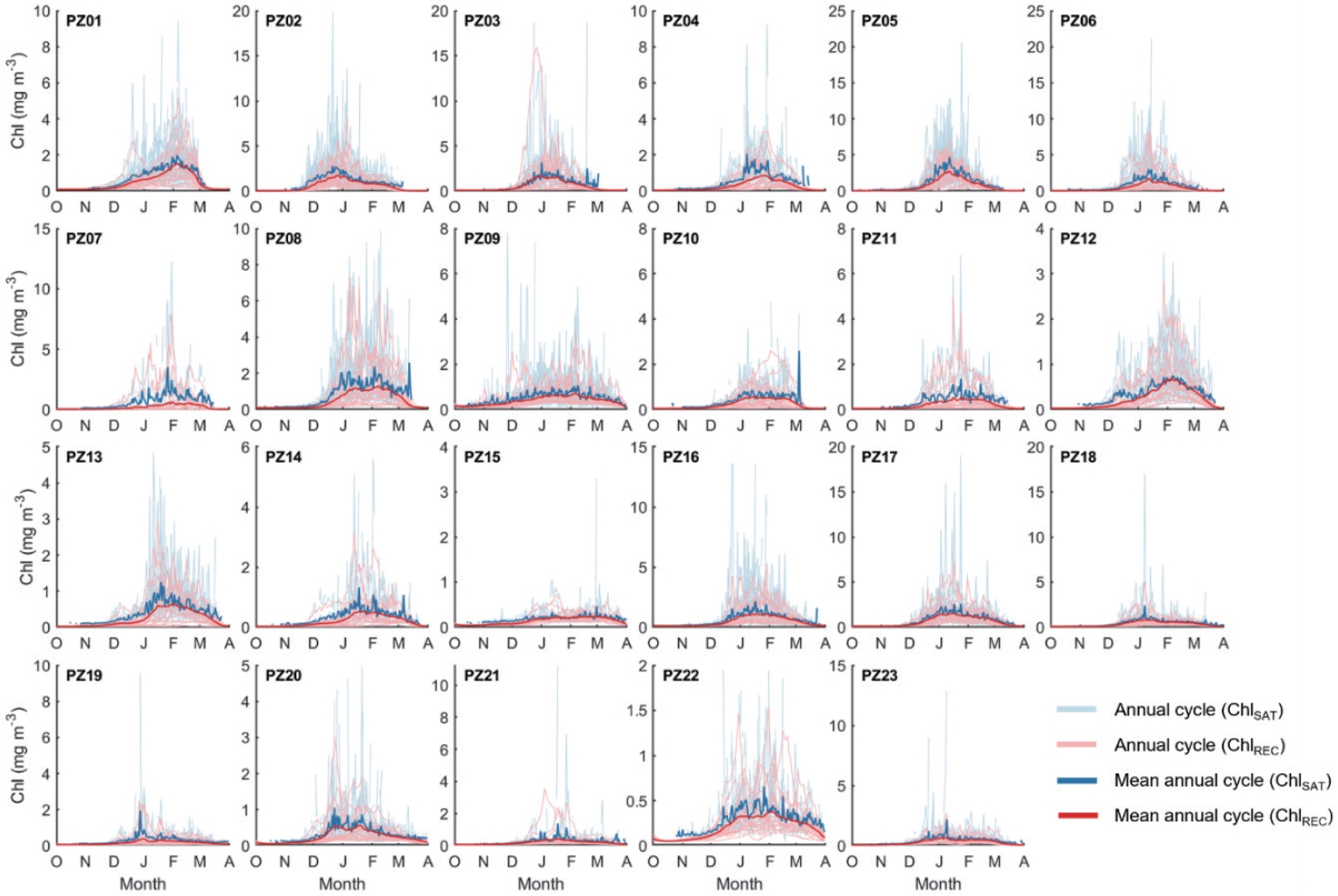
- Fig. 4는 23개의 폴리냐 지역에서 엽록소 농도의 연변화를 제시한 것이다. 평균적인 양상 측면에서 두 자료 간의 큰 차이는 나타나지 않는다. 다만 각 해마다의 변동성에는 상당한 차이가 발생한다. 특히 식물플랑크톤 번성이 시작되는 10-11월에 기존 위성 관측된 엽록소의 농도가 과대평가되어 있다. 이 시기에는 해빙이 녹기 시작하며 폴리냐 해역이 확장되기 시작하고 겨울철 대비 운량이 점차 줄어들어 일부 국한된 지역에 관측이 가능하게 되지만 구름의 가장자리 부분에서 나타날 수 있는 과대 추정치가 공간적 평균된 시계열 자료에 그대로 반영된 경우가 상당수 존재하는 것으로 확인되었다. 따라서 이는 실제 식물플랑크톤의 성장 패턴이라고 반영하기는 어렵다. 반면 복원 자료에서는 식물플랑크톤의 성장 곡선이 대체적으로 안정되게 나타나며 관측 자료 대비 약간 과소 추정되는 것으로 확인되었다. 원격 탐사 기반 일차생산 추정에 주요한 요소인 엽록소 농도의 관측 자료와 복원 자료 간의 격차가 매해 일정하지 않음을 감안할 때, 일차생산의 경년 변동성은 달라질 수 있으며, 이는 곧 경향에도 영향을 미칠 수 있다. 특히, 일차생산력 추정에 활용될 수 있는 공간 영역이 확장됨에 따라 그 결과는 기존의 결과와 상당한 차이를 발생시킬 것으로 판단된다.
3. 결과
- 본 연구는 남극 폴리냐 지역에서 실제 일차생산력에 근접한 추정치를 도출할 수 있도록 DINEOF를 이용하여 해색 위성 기반 엽록소 농도의 결측에 대한 복원을 수행하였으며, 엽록소 농도의 기존 및 복원 시계열 자료를 제공하고자 한다. 남극 폴리냐 지역에서 생성된 엽록소 농도의 복원된 자료는 향후 일차 생산성 추정에 사용되어 남극 연안 지역의 일차 생산을 담당하고 있는 폴리냐 지역에서 장기간 변동성 및 경향성에 대한 개선된 추론을 가능하게 할 것으로 기대한다.
4. 결론 및 토의
-
Conflict of Interest
Hyun-Cheol Kim has been an Editorial Board of GEO DATA; however, he was not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this paper. Otherwise, no other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this paper were reported.
-
Funding Information
This work was supported by Korea Institute of Marine Science & Technology Promotion (KIMST) grant funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries (KIMST 20220547).
Notes


| Criteria | Value |
|---|---|
| Ice free days | ≥20% |
| Bathymetry | <2,000 m |
| Latitude | <65o S |
| Valid data percentage per pixel | ≥5.65% |
- Arrigo KR, van Dijken GL, Strong AL (2015) Environmental controls of marine productivity hot spots around Antarctica. J Geophys Res Oceans 120(8):5545–5565ArticlePDF
- Beckers JM, Rixen M (2003) EOF calculations and data filling from incomplete oceanographic datasets. J Atmos Ocean Technol 20(12):1839–1856Article
- Deppeler SL, Davidson AT (2017) Southern Ocean phytoplankton in a changing climate. Front Mar Sci 4:40Article
- Gerringa LJ, Alderkamp AC, Laan P, et al (2012) Iron from melting glaciers fuels the phytoplankton blooms in Amundsen Sea (Southern Ocean): iron biogeochemistry. Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 71:16–31Article
- Gerringa LJA, Laan P, Van Dijken GL, et al (2015) Sources of iron in the Ross Sea Polynya in early summer. Mar Chem 177:447–459Article
- Kaufman DE, Friedrichs MA, Smith WO Jr, Hofmann EE, Dinniman MS, Hemmings JC (2017) Climate change impacts on southern Ross Sea phytoplankton composition, productivity, and export. J Geophys Res Oceans 122(3):2339–2359ArticlePDF
- Leung S, Cabré A, Marinov I (2015) A latitudinally banded phytoplankton response to 21st century climate change in the Southern Ocean across the CMIP5 model suite. Biogeosciences 12(19):5715–5734Article
- Li Y, Ji R, Jenouvrier S, Jin M, Stroeve J (2016) Synchronicity between ice retreat and phytoplankton bloom in circum‐ Antarctic polynyas. Geophys Res Lett 43(5):2086–2093ArticlePDF
- Park J, Kim JH, Kim HC, Hwang J, Jo YH, Lee SH (2019) Environmental forcings on the remotely sensed phytoplankton bloom phenology in the central Ross Sea Polynya. J Geophys Res Oceans 124(8):5400–5417ArticlePDF
- Pinkerton MH, Boyd PW, Deppeler S, Hayward A, Höfer J, Moreau S (2021) Evidence for the impact of climate change on primary producers in the Southern Ocean. Front Ecol Evol 9:592027Article
- Rickard G, Behrens E (2016) CMIP5 Earth system models with biogeochemistry: a Ross Sea assessment. Antarct Sci 28(5):327–346Article
- Smith WO Jr, Comiso JC (2008) Influence of sea ice on primary production in the Southern Ocean: a satellite perspective. J Geophys Res Oceans 113(C5):C05S93Article
References
Appendix
Figure & Data
References
Citations


 GAIDAS
GAIDAS
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite